11-02. セルオートマトン
02-01.ルール178を実装してみよう¶
# 02-01-01. ルール178
def rule178(cell1, cell2, cell3):
if cell1 == 0:
if cell2 == 0:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 1
elif cell2 == 1:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 0
elif cell1 == 1:
if cell2 == 0:
if cell3 == 0:
return 1
elif cell3 == 1:
return 1
elif cell2 == 1:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 1# 確認
for cell1 in range(2):
for cell2 in range(2):
for cell3 in range(2):
print(cell1, cell2, cell3, ": ", rule178(cell1, cell2, cell3))0 0 0 : 0
0 0 1 : 1
0 1 0 : 0
0 1 1 : 0
1 0 0 : 1
1 0 1 : 1
1 1 0 : 0
1 1 1 : 1
# 02-01-02. セルオートマトンの実行
# パッケージの読み込み等
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num_cell = 100 # セルの数
steps = 50 # 何ステップまで計算するか
cell_list = [] # 各世代のセルの情報を記録するリスト
cell = np.zeros(num_cell, dtype=int) # セルの初期化
cell[int(num_cell / 2)] = 1 # 一つのセルだけに1を代入
cell_list.append(cell)
for t in range(steps):
# -- 状態遷移 --
cell_tmp = np.ones(num_cell, dtype=int)
# 境界条件処理その1
cell_tmp[0] = rule178(cell[num_cell - 1], cell[0], cell[1])
# メイン
for i in range(1, num_cell - 1, 1):
cell_tmp[i] = rule178(cell[i - 1], cell[i], cell[i + 1])
# 境界条件処理その2
cell_tmp[num_cell - 1] = rule178(cell[num_cell - 2], cell[num_cell - 1], cell[0])
# 情報の更新
cell = np.copy(cell_tmp)
cell_list.append(cell)# 02-01-03. セルオートマトンの可視化
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.matshow(cell_list[:], cmap="binary")<Figure size 1920x1440 with 0 Axes>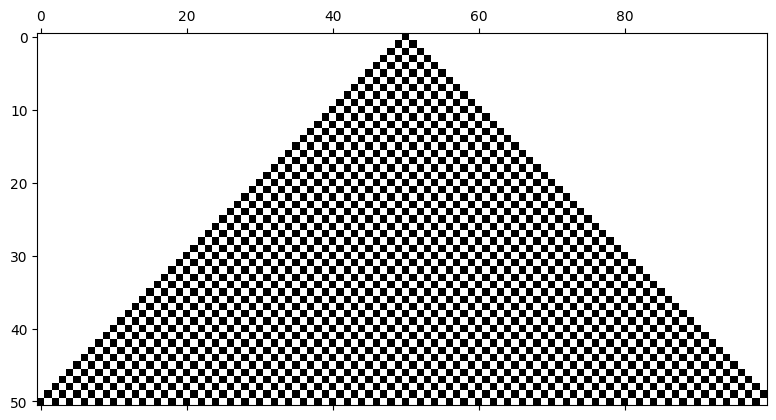
02-02 別のルールを実装してみよう¶
ルール0(クラス1)¶
Solution to Exercise 1
すべての場合で0を返せば良い.
# 02-02a. ルール0
def rule0(cell1, cell2, cell3):
if cell1 == 0:
if cell2 == 0:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 0
elif cell2 == 1:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 0
elif cell1 == 1:
if cell2 == 0:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 0
elif cell2 == 1:
if cell3 == 0:
return 0
elif cell3 == 1:
return 0rule0を使って同様にシミュレーションしてみよう.
num_cell = 100
steps = 50
cell_list = []
cell = np.zeros(num_cell, dtype=int)
cell[int(num_cell / 2)] = 1
cell_list.append(cell)
for t in range(steps):
# -- 状態遷移 --
cell_tmp = np.ones(num_cell, dtype=int)
# 境界条件処理その1
cell_tmp[0] = rule0(cell[num_cell - 1], cell[0], cell[1])
# メイン
for i in range(1, num_cell - 1, 1):
cell_tmp[i] = rule0(cell[i - 1], cell[i], cell[i + 1])
# 境界条件処理その2
cell_tmp[num_cell - 1] = rule0(cell[num_cell - 2], cell[num_cell - 1], cell[0])
# 情報の更新
cell = np.copy(cell_tmp)
cell_list.append(cell)
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.matshow(cell_list[:], cmap="binary")<Figure size 1920x1440 with 0 Axes>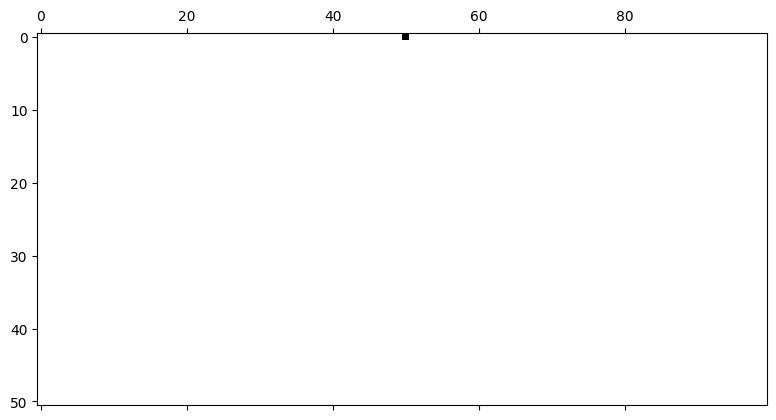
(初期状態の一行目を除いて)常にすべて白となる.
様々なルールへ対応する¶
Solution to Exercise 2
まず任意のルールに対応できる関数を定義する.
2状態1次元1近傍セルオートマトンのルール総数はあり, セルの状態がからを2進数の8桁にそれぞれ対応させ,各桁の値を遷移後の状態とする.
# 任意のルールに対応できる関数
def rule(rule_num, cell1, cell2, cell3):
rule_list = []
mod = rule_num
for i in range(8):
k = 7-i
q, mod = divmod(mod,2**k)
rule_list.append(q)
idx = 4*cell1+2*cell2+cell3
cell2_new = rule_list[7-idx]
return cell2_newdivmode(p, q)はpをqで割ったときの,と余りを返す関数.
これを使ってルールのセット rule_list を作成する.
各要素はからまでの遷移ルールに対応する.
rule_numにルール番号を与えることで任意のルールに基づいた遷移が実行される.
rule()を使ってシミュレーションをする関数を定義する.
def run_ca(rule_num = 178, n_cells = 100, n_steps = 200):
cell_list = []
cell = np.ones(n_cells,dtype=int)
cell[int(n_cells/2)] = 0
cell_list.append(cell)
for t in range(n_steps):
# -- 状態遷移 --
cell_tmp = np.ones(n_cells,dtype=int)
# 境界条件処理その1
cell_tmp[0] = rule(rule_num, cell[n_cells-1],cell[0],cell[1])
# メイン
for i in range(1,n_cells-1,1):
cell_tmp[i] = rule(rule_num, cell[i-1],cell[i],cell[i+1]);
# 境界条件処理その2
cell_tmp[n_cells-1] = rule(rule_num, cell[n_cells-2],cell[n_cells-1],cell[0]);
# 情報の更新
cell = np.copy(cell_tmp)
cell_list.append(cell)
return cell_listこれを使ったルール0を実行する.
cell_list = run_ca(rule_num = 0, n_cells = 100, n_steps = 50)
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.matshow(cell_list[:], cmap="binary")<Figure size 1920x1440 with 0 Axes>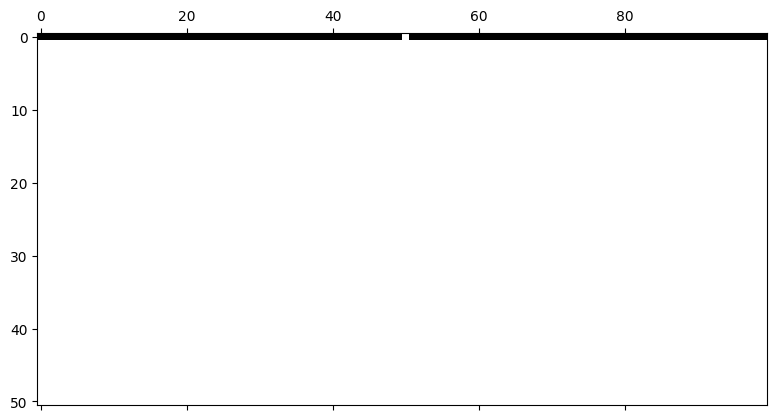
Solution to Exercise 3
ルール90(クラス2)¶
# 02-02a. ルール90
cell_list = run_ca(rule_num = 90, n_cells = 200, n_steps = 100)
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.matshow(cell_list[:], cmap="binary")<Figure size 1920x1440 with 0 Axes>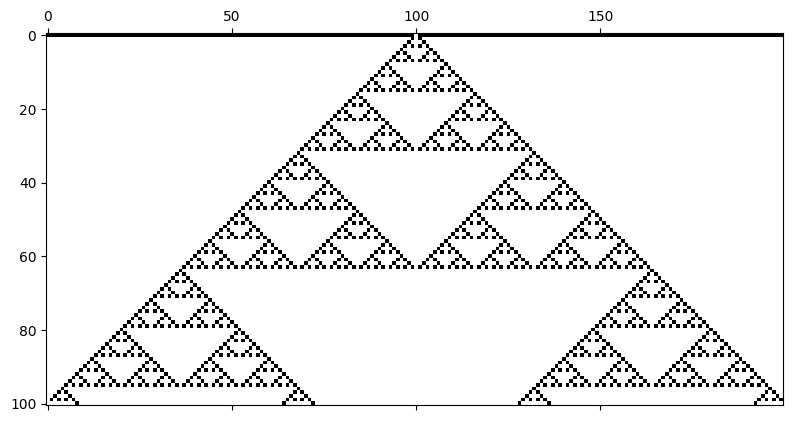
ルール30(クラス3)¶
# 02-02c. ルール30
cell_list = run_ca(rule_num = 30, n_cells = 200, n_steps = 100)
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.matshow(cell_list[:], cmap="binary")<Figure size 1920x1440 with 0 Axes>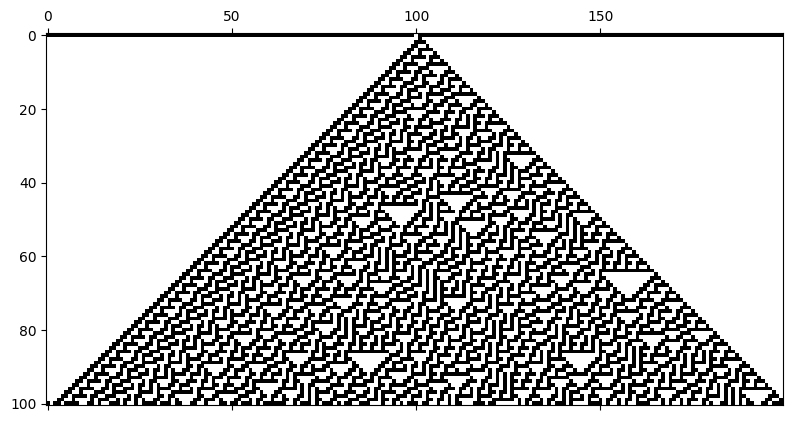
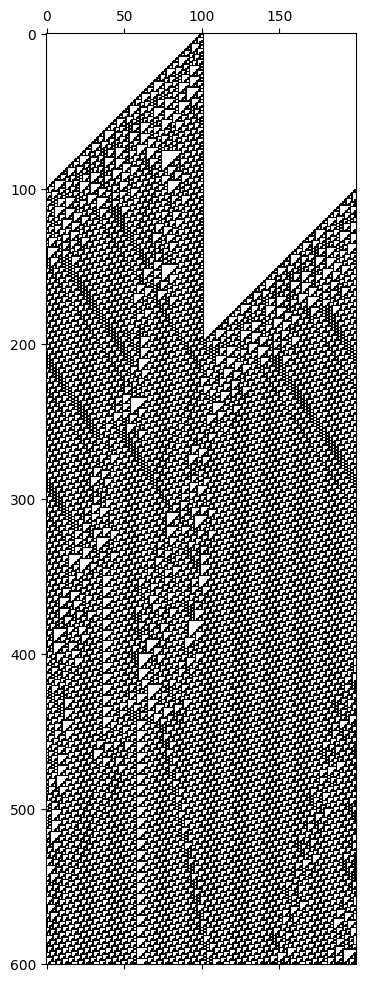
ルール110(クラス4)¶
# 02-01-01. ルール178
cell_list = run_ca(rule_num = 110, n_cells = 200, n_steps = 600)
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.matshow(cell_list[:], cmap="binary")<Figure size 1920x1440 with 0 Axes>